“Twenty-first century citizens live in an interconnected, diverse and rapidly changing world. Emerging economic, digital, cultural, demographic, environmental forces and global diseases (like COVID-19) are shaping everyone’s lives around the planet, and increasing intercultural encounters on a daily basis. To cope with this complex environment, it is urgent to foster global competence and equip all, not only the adults of tomorrow, but also the adults of today, with the necessary know-how and tools to use global competence (Isabel Nunes, Mindshift) and therefore, to promote global social change”.
Sociologists define social change as changes in human interactions and relationships that transform cultural and social institutions. These changes occur over time and often have profound and long-term consequences for society. Well known examples of such change have resulted from social movements in civil rights, women’s rights, and LBGTIQ+ rights, to name just a few. Relationships have changed, institutions have changed, and cultural norms have changed as a result of these social change movements.
On the other hand, the Asia Society and Council of Chief State School Officers define Global Competence as “the capacity and disposition to understand and act on issues of global significance”.
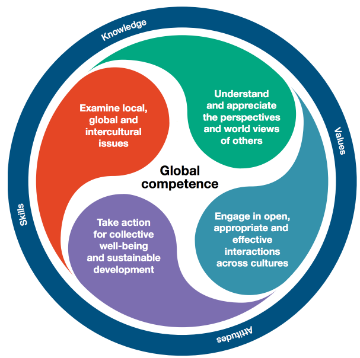
The Longview Foundation also adds that Global competence is “a body of knowledge about world regions, cultures and global issues, and the skills and dispositions to engage responsibly and effectively in a global environment” is also needed.
Why do we need global competence?
As stated before, we live in a complex and rapidly changing world:
- World events and global issues are complexand interdependent.
- One’s own culture and history is key tounderstanding one’s relationship to others
- A broad range of forces are transforming the global landscape requiring people new capacities and dispositions: changing demands of work; migration and immigration creating more culturally and linguistically diverse societies;climate instability and the growing need for global environmental stewardship.
- Over the last decades numerous reports and policy statements have emphasized the need for new skills for the 21st century.

Global competence, a multidimensional capacity
According to the OECD PISA global competence framework, global competence is a multidimensional capacity and comprises:
- Living harmoniously in multicultural communities
- Thriving in a changing labour market
- Using media platforms effectively and responsibly
- Supporting the Sustainable Development Goals
- Pursuiting lifelong learning and stay curious, open and get active
Becoming globally competent to promote social change
Following there are listed some features of globally competent people by David Young, VIF International Education.
- Appreciation of culture. Understanding own and others’ culture.
Watch this video by the Intercultural English Channel to learn more about culture.
The Cultural Iceberg: https://youtu.be/a9Z83I_g4Hw
- Evaluation of information. Questioning information and looking for deeper understanding.
- Cross cultural communication. Effectively change ideas with people with different backgrouds, virtually or in presence. Effective communication and appropriate behaviour within culturally diverse teams are keys to success in many jobs. It can boost employability.
You can watch this other video by Julian Treasure where he explains “Fiveways for conscious listening to other people and the world around you”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cSohjlYQI2A
- Perspective taking skills. Demonstrating curiosity, empathy, tolerance and respect and showing compasion for the perspective of others.
- Intelligent humility. Recognizing that there is a lot to learn about the world.
- Divergent thinking. Seeing alternatives and new solutions to existing problems.
- Technological literacy. The transformations in digital technologies have shaped people interactions and new types of learning. It requires using media platforms effectively and responsibly and also to communicate and collaborate with others.
Globally competent citizens are global minded, one sees oneself as connected to the world community and feels a sense of responsibility for its members(Hett cited in Hansen, 2010). Global mindness contributes to the development of a social change global perspective.

Developing skills to better engage the world
Becoming globally competent is a matter of education and it can be trained.
We can list some skills to better engage the world in order to also promote them in our environments and working contexts: Initiative, Enthusiasm, Inquisitiveness, Courage, Self-reliance, Self-Confidence, Self-control, Self-knowledge, Positive outlook toward adversity, Independence, Appreciation of diversity, Perseverance, Creativity, Flexibility, Comfort with uncertainty, Open Mindness, Language and communication skills, Assertiveness, Sense of humor.
Social changes involve individuals. Educating individuals for global competence can be a tool for bringing people together and generating social change.







